Vol.11 Issue 2 / Latest topics 5Revolution in Predicting Previously Undetermined Structures of Organic Compounds
-
Our daily lives are overflowing with organic compounds all around us,such as in foods, pharmaceuticals, plastics, detergents, and cosmetics.The characteristics of those compounds vary significantly depending on the number and position of carbon-carbon double bonds. The position of carbon double bonds was previously difficult to determine, such as in lipid research, but oxygen attachment dissociation (OAD), an ion dissociation technology developed by Shimadzu, now enables the position of carbon double bonds to be inferred. The following describes
the OAD-TOF system, an analytical solution expected to cause revolutionary changes in society in the near future with technology developed for the first time in the world at the Koichi Tanaka Mass Spectrometry Research Laboratory.From Conventional Constraints to Cutting-Edge Innovations
With conventional mass spectrometry technology, it was sometimes difficult to analyze the structures of compounds in detail. In particular,determining the position of carbon–carbon double bonds while retaining the native structure of lipids and other complex organic compounds was challenging. Due to the demand for more detailed structural information in chemical and biotechnology fields, there was an urgent need to develop new technology for structural analysis.
The Koichi Tanaka Mass Spectrometry Research Laboratory at Shimadzu Corporation developed OAD technology that can use oxygen radicals to dissociate double bonds between carbons specifically.
That OAD technology enables detailed structural analysis that was difficult to achieve with conventional methods. Using cutting-edge mass spectrometry research results, the laboratory provided support throughout the OAD development process from basic research to product commercialization.
The typical technique used for structural analysis of molecules in samples by mass spectrometry involves ionizing the target molecule and colliding it with an inert gas, such as argon, referred to as collision-induced dissociation (CID), and then analyzing the dissociated ion fragments. CID is widely used as a generic technique, but it can result in some parts of molecules not dissociating, which can prevent obtaining sufficient structural information for analyzing some targets, such as post-translational modifications of proteins. In response, the Koichi Tanaka Mass Spectrometry Research Laboratory developed the world’s first technique for fragmenting ions by inducing direct collisions between the ions and highly reactive atomic hydrogen (hydrogen radicals) or atomic oxygen (oxygen radicals). Both the hydrogen attachment/abstraction dissociation (HAD) method, which uses hydrogen radicals, and the oxygen attachment dissociation (OAD) method, which uses oxygen radicals, have attracted significant interest as revolutionary technologies that provide extensive information useful for structural analysis of biological samples.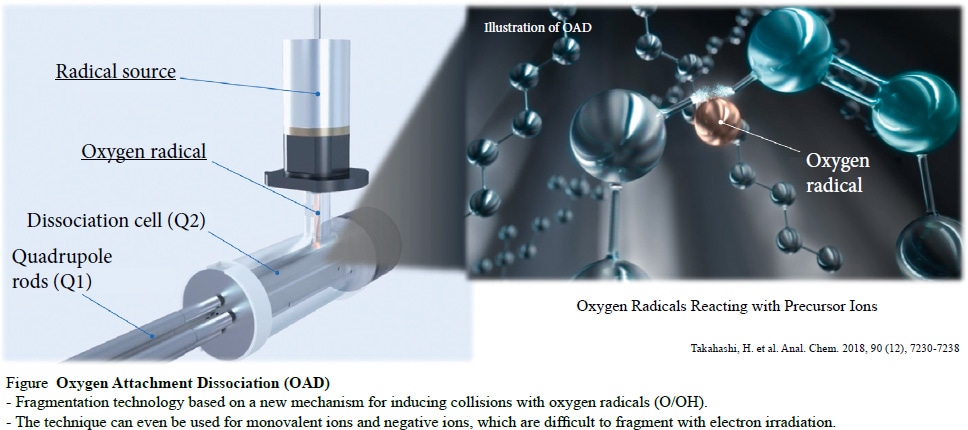
Diverse Applications of OAD Technology
In December 2023, Shimadzu Corporation released the OAD-TOF quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer system based on those key technologies, the first system in the world to achieve detailed structural analysis of lipids and other natural compounds. By using Shimadzu’s unique OAD ion dissociation technology to infer the positions of carbon double bonds, which was previously difficult to do, by measuring the size and quantity of sample substances separated down to the atomic and molecular level, and by using that information in combination with accurate compound information obtained with a quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer (Q-TOF MS) system, structures can be identified in lipids, natural substances, and a wide variety of other compounds.
- IMSC 2024 / Related Applications -IMSC2024
- Dual fragmentation via collision-induced and oxygen attachment
dissociations using water and its radicals for C=C position-resolved lipidomics
Examples of Using the Product/Technology
• Lipid Analysis: OAD technology is especially useful for determining the positions of carbon double bonds in lipids. Consequently, it has helped provide new knowledge about the functions and activity of lipids, which has been useful for developing new drugs and diagnosing diseases.
Example: Analyzing the positions of lipid double bonds in mouse liver In this example, detailed structural information was obtained from a single analysis of lipids contained in a mouse liver extract.• Structural Analysis of Organic Compounds: The ability to perform detailed structural analysis of complex organic compounds contributes to the development of new functionally beneficial compounds and clarification of biological phenomena.
Example: Analyzing the positions of triacylglycerol double bonds in butter This is an example of quickly analyzing the positions of triacylglycerol (TG) double bonds in butter.Feedback and Future Developments Across Various Fields and Industries
At the International Mass Spectrometry Conference 2024 (IMSC 2024) Shimadzu gave an oral presentation on some of the latest OAD applications.It was introduced that the functionality for analyzing OAD spectra was included in MS-DIAL 5 data analysis software*1 developed by Professor Tsugawa of Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology,and the functionality can be used for lipid profiling or automatic analysis of lipid structural isomers. Attendees showed particular interest in the broad applicability of the automatic data analysis workflow using MS-DIAL 5 to automatically analyze OAD spectra without changing any pretreatment or chromatography settings and the higher sensitivity achieved by the OAD method compared to other techniques.
Professor O’Hair’s group from the University of Melbourne gave a presentation on technology for structural analysis of PFOA-related compounds using OAD. It was the first time that OAD was shown to provide product ions from PFOA-related compounds based on a different dissociation mechanism than CID. That resulted in many questions and comments from many participants involved in environmental analysis or predicting the structures of complex compounds, such as branched chains, and stimulated an exchange of views about possible application fields.
Shimadzu remains committed to continue contributing to research advancements in healthcare and life science fields by offering new products.