LC/MS/MS Method Package for Glycosaminoglycan
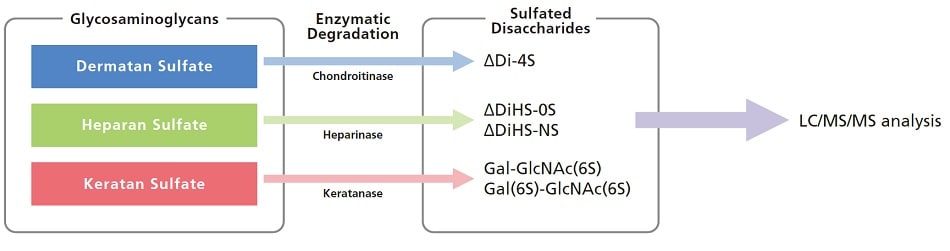
The study of Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides, and enzymes involved in GAG metabolism is an important aspect of clinical research related to lysosomal storage. Quantitation of GAGs in bones, joints, the brain, heart, lungs, and other organs is a useful tool in this field of study. GAGs can be quantitated by measuring the sulfated disaccharides produced by enzymatic degradation of GAGs. The research group led by Hironori Kobayashi of Shimane University Hospital, Clinical Laboratory Division, has been instrumental in the development of methods for the detection of sulfated disaccharides by LC/MS.
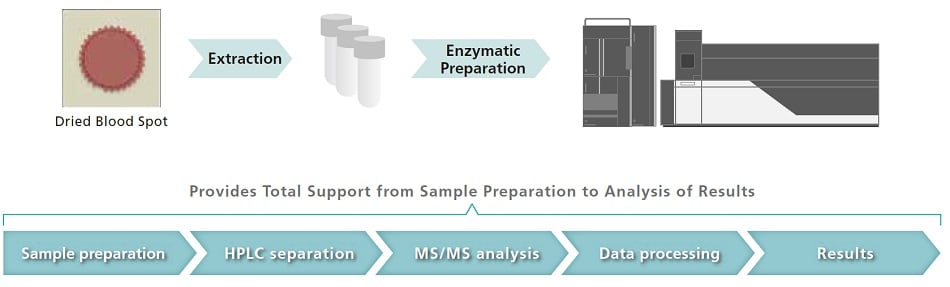
The LC/MS/MS Method Package for Glycosaminoglycans contains LC/MS/MS analytical methods with optimized separation conditions and MS parameters for sulfated disaccharides derived from six important glycosaminoglycans. It also has example sample preparation protocols for blood spots, including enzymatic preparation. This method package can be used to analyze glycosaminoglycans while saving significant time in the development of sample preparation and analytical protocols.
LC/MS/MS Method Package for Glycosaminoglycans
- Example sample preparation protocols for dried blood spots
- Analytical conditions for highly robust chromatography
- Optimized MS/MS parameters
- Methods compatible with LCMS-8060 series and LCMS-8060NX systems

Workflow from analyte extraction from dried blood spot to LC/MS/MS analysis
Glycosaminoglycans and Sulfated Disaccharides
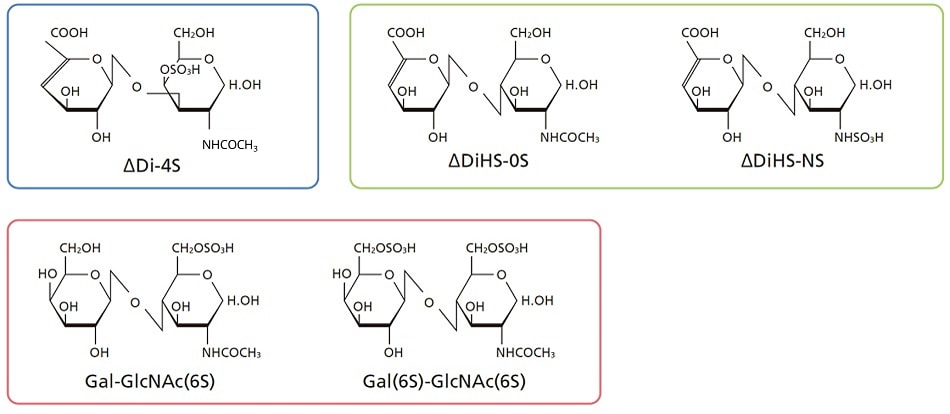
Examples of Sulfated Disaccharides Detected by this Method Package
Remarks and Precautions
- Requires LabSolutions LCMS Ver. 5.113 or later.
- This method package is intended for research use only. It may not be used for clinical diagnostic applications.
Note: LabSolutions is a trademark of Shimadzu Corporation or its affiliated companies in Japan and/or other countries.
News / Events
-
Shimadzu has released the Shim-vial™ H glass, S glass.
Shimadzu provides high-quality vials that thoroughly eliminate these risks by visually inspecting each vial, allowing them to be used with confidence.
-
INTERNATIONAL MASS SPECTROMETRY CONFERENCE 2024
Visit the Shimadzu booth at the International Mass Spectrometry Conference (IMSC) 2024.
-
Metabolomics 2024
Shimadzu Lunch Presentation at Metabolomics 2024
Date: June 20th, 2024 (Thursday)
Time: 12:25 – 1:25 p.m. -
New LabSolutions Insight Biologics
Supporting Innovation with Oligonucleotide Therapeutics
-
Shimadzu has released the LCMS-TQ RX Series High-Performance Liquid Chromatograph Mass Spectrometers
Innovative technology, exceptional design and new ways of thinking are part of our engineering DNA delivering solutions for the ever-changing needs of any laboratory. As our scientific and business needs change our engineering design evolves and adapts. The result is the RX Series of triple quadrupole LC-MS instruments designed with unmatched capability, redefined reliability and creating a new standard in actionable data.
-
Three Analytical and Measuring Instruments Win the Internationally Recognized “iF Design Award 2024”
The Shimadzu LCMS-2050 high-performance liquid chromatograph mass spectrometer, the Brevis GC-2050 gas chromatograph, and the ICPMS-2040/2050 ICP mass spectrometer won the internationally recognized iF Design Award 2024 in the product design category.



