Analysis of Gasoline Components (GC)
With the abolition of the Japanese Provisional Measures Law on the Importation of Specific Refined Petroleum Products in March 1996, the concentration of methanol, MTBE (methyl tertiary-butyl ether), benzene, and kerosene (equivalent to 14 times the total content of n-C13 and n-C14) was prescribed. Four different gas chromatography measurements are prescribed as analytical methods for these controlled components in JIS K 2536-1996 (Liquid petroleum products -- Testing method of components).
"Total components testing method by gas chromatography" is introduced below.
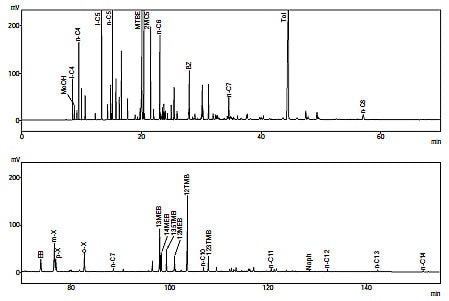
Analysis of Gasoline Components (GC)
Gas Chromatograph

A gas chromatograph (GC) measures the content of various components in a sample. The sample solution injected into the instrument enters a gas stream, which transports the sample into a separation tube known as the "column." Helium or nitrogen is used as this so-called carrier gas. The components are separated inside the column, and a detector measures the quantity of the components that exit the column. To measure a sample with an unknown concentration, a standard sample with a known concentration is injected into the instrument. The standard sample peak retention time (appearance time) and area are compared to the test sample to calculate the concentration.


