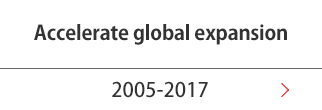1917
Japan Storage Battery Co., Ltd. (today’s GS Yuasa Corporation) was established to specialize in battery production

Shimadzu was reorganized as joint stock company with Genzo Jr. as president
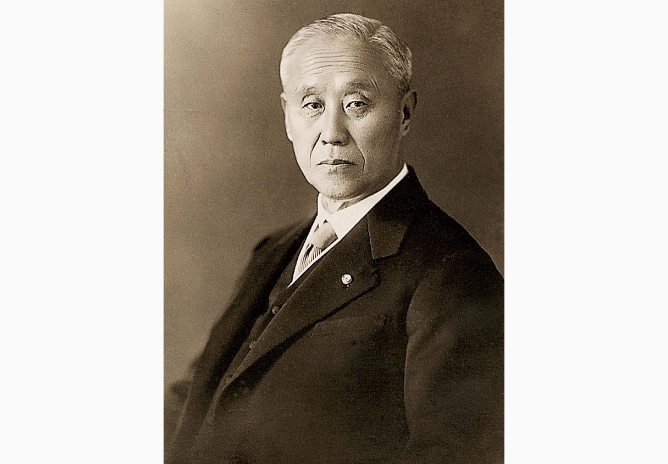

Testing equipment manufacturing began
Shimadzu bolstered its foundation in testing equipment by introducing a fiber-testing device as a physics and chemistry instrument. Two years later, with guidance from Prof. Matsumura of Kyoto Imperial University, the company commercialized a repetitive-impact testing machine, followed by an Amsler-type hydraulic-pressure tester and a Schopper-type tensile testing machine.
1918
Shimadzu launched Diana medical X-ray system
X-ray machines became more widespread in the 1910s, and Shimadzu developed a succession of new products. Among them, the Diana X-ray machine was improved continuously after its launch and was an established seller through the mid-1930s. As ease of operation improved, sales exploded not only in Japan but internationally. The Diana was also useful in diagnosing tuberculosis and benefitted many patients.

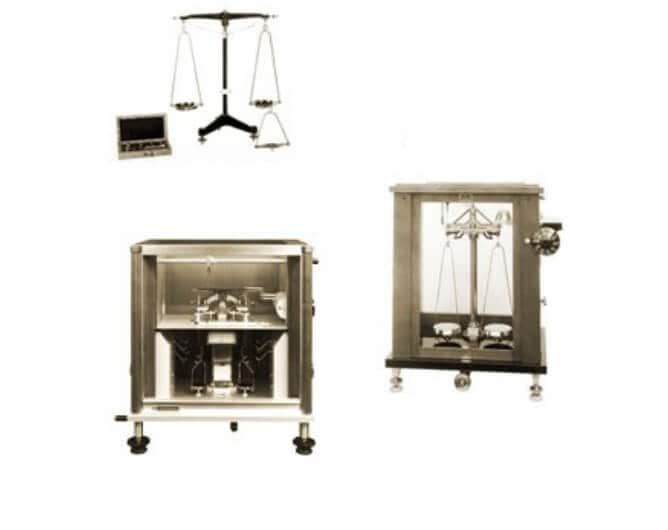
Balance scale manufacturing began

1920
Gear coupling manufacturing began
1921
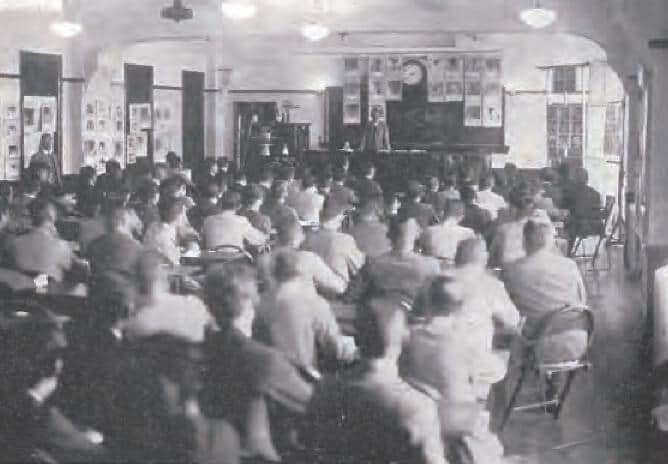
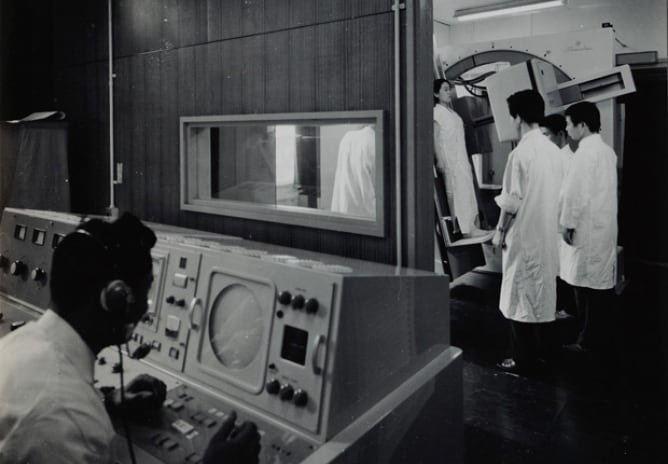
First X-ray was held
Shimadzu held the first X-ray at its Kawaramachi main office. Medical treatment using X-rays was still a new field, and dissemination of the correct knowledge concerning X-rays, and acquisition of expertise in operating X-ray devices, were important goals in the field of radiology.

1923
Berlin Branch Office was established

1925
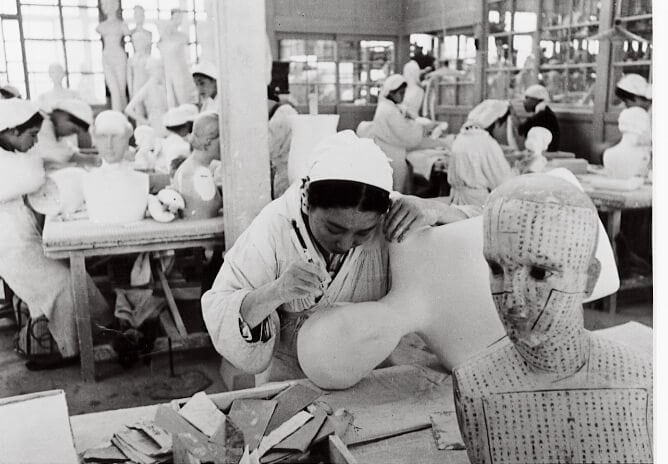
Mannequin manufacturing began
The trend toward Western-style clothing was accompanied by an increase in mannequin imports, but many of these mannequins were damaged during shipping. In response, Shimadzu utilized the technology it developed for making human body models in the Specimen Department to repair and manufacture mannequins. At its peak, the company was producing over 85% of mannequins in Japan. The business continues today under the auspices of another company.

1926
Textile machinery (spinning pumps and nozzles) manufacturing began
1927
Shimadzu X-ray Technology Training Center (now Kyoto College of Medical Science) opened
The center developed specialist technicians with correct X-ray related knowledge and skills. The training period was six months. Graduates of junior high schools or above were recruited from across the country and tested. The first intake totaled 40 students, 20 in the main course and 20 auditors.
1930
Shimadzu President Genzo Shimadzu Jr. was named one of Japan’s ten greatest inventors
Genzo Jr. was named one of the ten greatest inventors in Japan in recognition of his Simple Applied Method for Manufacturing Lead Powder, an important material for storage batteries. The method delivered significant improvements and cost reductions in the production of lead powder, at a time when Japan was largely dependent on imports of this material.

1933
Industrial X-ray apparatus (WELTES) manufacturing began

1934
Optical analyzer (spectrograph) and X-ray analyzer manufacturing began
1936
Aircraft equipment manufacturing began

1937
Shimadzu Seisakusho Seinen Gakko (now Shimadzu Engineering School) was established

1940
Process control instrument manufacturing began

First issue of Shimadzu Review was published