Carbon Nanotube | Purity | Qualification of Metal Catalysts
Typical methods for producing carbon nanotubes (CNTs) include arc discharge, laser ablation, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). As each method employs a catalyst to promote the growth of CNTs, purification is required after production. Metal impurities can be eliminated by acid treatment but trace levels of metals can remain if purification is inadequate.
X-ray fluorescence measurement data for multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) and carbon nanofibers (CNFs) is shown below.
X-ray fluorescence spectrometry permits the easy, non-destructive, simultaneous analysis of multiple elements. It allows the simple quantitation of catalyst metal elements and residues from acid treatment in CNTs. Approximately 0.1 g sample is required for measurement, but the entire amount can be recovered. Precise quantitation is possible if standard samples are available.
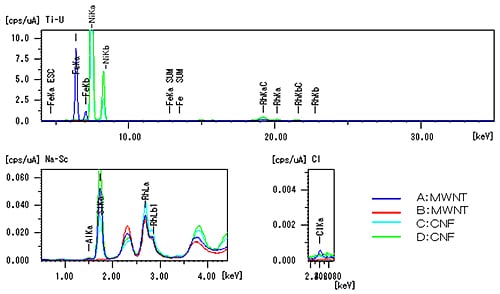
X-ray Fluorescence Analysis of MWNTs and CNFs (Instrument: EDX-700HS)
Energy Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer

X-Ray fluorescence spectrometry permits the easy, non-destructive, simultaneous analysis of multiple elements. It is effective for measurements where only a small sample volume is available or where the sample is valuable and cannot be lost. It allows the simple quantitation of catalyst metal elements (Co, Ni, Y, La, Fe, Rh, Pt, etc.) and the quantitation of residues from acid treatment (S, Cl) in CNTs. Approximately 0.1 g sample is required for measurement, but the entire amount can be recovered. Precise quantitation is possible if standard samples are available.


