Observations of the High-Speed Breakage in CFRPs
Observations of the High-Speed Breakage in CFRPs
DIC Based Ultra-High-Speed Strain Distribution Visualization System - CFRP High-Speed Tensile Tests and DIC Analysis
In recent years, analyzing structural damage utilizing FEM (finite element method) analysis and other techniques has been used in product design in order to shorten the product development cycle, reduce prototype costs, and reduce the cost of strength testing of components. To improve the accuracy of damage analysis, the necessity of evaluating the correlation between actual tests and analysis results will be heightened. A strong demand is also anticipated for so-called solutions technologies capable of evaluating the breakage behavior of components and visualizing in-plane strain distributions, phenomena that are difficult to measure with existing techniques. Introduced below is the attainment of DIC analysis in high-speed tensile tests using the HPV-X system, which satisfies the requirements of imaging speed and resolution.
CFRP
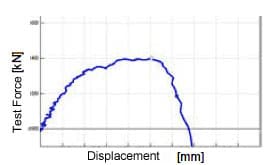
CFRP (carbon-fiber reinforced plastics) and other fiber reinforced composite materials are characterized by remarkable strength and lightness, and are widely used as a material for aircraft parts. Their subsequent expanded application in automobiles and a variety of other products is expected. With CFRP, it is known that breakage progresses with the damaged area as the starting point, and when the maximum test force is reached, high-speed brittle fracture is seen. Clarifying the details of this breakage process is extremely important to the construction of damage analysis models.
Test Example
High-Speed Tensile Testing
High-Speed Breakage Observations (video recording speed: 500,000 frames/sec)
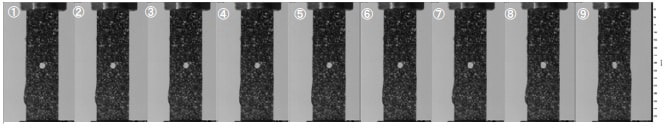
The breakage process can be observed. It is evident that cracks have developed in the vicinity of the circular holes. Furthermore, DIC analysis reveals the strain distribution prior to breakage.
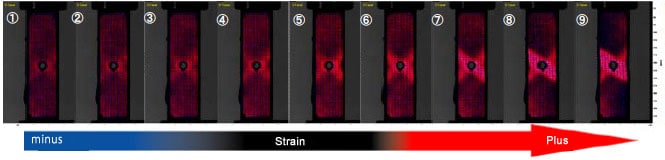
Two-dimensional mapping for the strain in the sample observation plane
System Overview

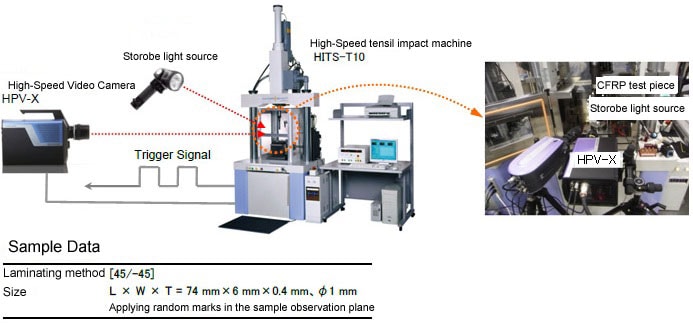
Hydroshot HITS-T10 High-Speed Tensile Testing System
Sampling test force data at 1 MHz
Saves up to 12,000 data points at 1 MHz.
Capable of detecting fractures reliably
Fracture is detected with a load amplifier (or strain gauge), and the trigger signal is transferred to the high-speed video camera.
DIC analysis System
Breakage of the material is precisely observed by high-speed video recording.
Synchronized with the HyperVision high-speed video camera.
The process of material breakage can be clarified through observations in the high time resolution region.
Displacement measurement & in-plane strain measurement
Displacement measurement and the two-dimensional strain mapping can be done based on image data from the high-speed video camera.
Non-contact type
Measurements can be performed without affecting the sample.
DIC (digital image correlation)
In this method, a random pattern on the surface of an object is compared before and after the object is deformed, in order to investigate the degree of pattern movement. This method can be used for strain analyses of components under high temperatures, large structures, and microscopic components under a microscope.
High-Speed Puncture Impact Testing Machine

As calls for safety and improved reliability increase, it has become increasingly important to evaluate the dynamic strength (impact characteristics) of materials and parts. This tester can obtain data on maximum test force, energy, and displacement at a maximum speed of 72 km/h (20 m/s). Two models are available: a punch type (HITS-P10) and a tensile load type (HITS-T10).
High-Speed Video Camera

Equipped with Shimadzu's proprietary FTCMOS high-speed CMOS image sensor, this camera achieves ultra-high-speed continuous video recording of up to 10,000,000 frames per second. The memory capacity has also been expanded, enabling storage of up to 256 image frames. Furthermore, at up to 5 million frames/second, video can be taken with a maximum resolution of 400 x 250 pixels, enabling detailed analysis of samples.