Alkyl Mercury Compounds
Two methods are available for the measurement of mercury in the environment: total mercury measurement by UV absorption and atomic absorption spectrometry, and organomercury measurement by GC.
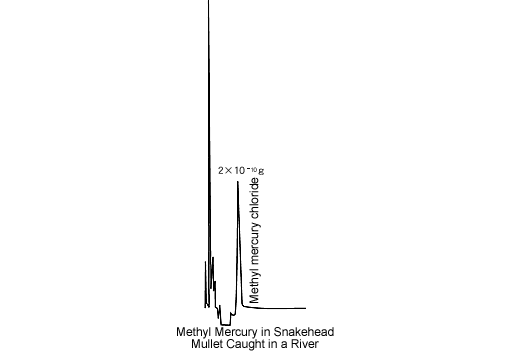
Measurement by GC is known to be an effective method for the analysis of organomercury, which is the cause of Minamata disease. As most organomercury exists in the environment as methyl mercury or ethyl mercury, chlorination permits highly sensitive and selective detection using an electron capture detector (ECD).
Gas Chromatograph

This separation/analysis instrument is widely used for the quantitative analysis of chemical substances. It is used with a detector and column combination that suits the analysis target components.


