Biomarker Searching | Analysis of Methylated DNA
Biomarker Searching
Analysis of Methylated DNA
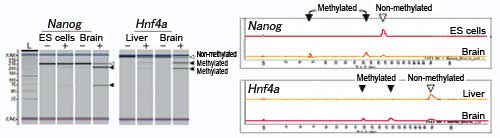
■ DNA methylation analysis by the COBRA method on theNanogandHnf4agenes in embryonic stem cells, brain cells, and liver cells
The phenomenon of changes in gene function that continue after cell division with no changes in the base sequence is known as epigenetics. It is becoming clear that epigenetic abnormalities in genes are involved in cancer and numerous other diseases.
Methylated DNA is one type of epigenetic gene control. It is anticipated to provide a biomarker for ES and iPS cell screening for disease diagnosis and regenerative medicine.
This is an example of DNA methylation analysis by the COBRA method on the Nanog and Hnf4a genes in embryonic stem (ES) cells, brain cells, and liver cells. The MultiNA Microchip Electrophoresis System for DNA/RNA Analysis was used for this analysis.
*COBRA: COmbined Bisulfite Restriction Analysis
Gel Images and Electropherograms
TheNanoggene, important for maintaining pluripotency of embryonic stem (ES) cells, shows low methylation in ES cells but high methylation in the brain. TheHnf4agene, involved in liver-specific gene expression, shows low methylation in the liver but high methylation in the brain.
* Data supplied by Prof. Shiota, Graduate School of Agricultural and Life Sciences, Tokyo University
DNA methylation analysis can be performed using several analytical methods, including bisulfite sequencing. However, the COBRA method offers low cost and high throughput, making it effective for screening and selecting samples for sequencing.
Microchip Electrophoresis System for DNA/RNA

DNA and RNA samples are separated by size by the electrophoresis system using a microchip so that the size of nucleic acid (DNA/RNA) samples is verified and approximately quantitated. The microchip achieves an electrophoresis system capable of speedily conducting electrophoresis separation, and a fluorescent detector ensures that analysis is performed to high sensitivity and, moreover, fully automatically.


