Analysis of Peptide Nucleic Acids (PNAs) using the MALDI-8020 benchtop linear MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer
Matrix assisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of- flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) is gaining popularity due to the ability of MALDI-MS to quickly provide information on accurate molecular mass using a simple sample preparation workflow. The MALDI-TOF MS can be used to confirm and guide synthesis of PNA oligomers, either in QC or R&D laboratories. Here, we demonstrate the analysis of three PNA samples using MALDI-8020 benchtop linear MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer.
Peptide Nucleic Acids (PNAs) are synthetic mimicking analogues of DNA oligomers where the nucleobases (A/G/C/T) are retained but the backbone of deoxyribose and phosphate blocks are replaced by peptide-like structures (Fig. 1). These structures are N- (2-amino-ethyl) glycyl units held together by peptide bonds which are neutral and achiral in nature, unlike the negatively charged sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA.
The charge state difference enhances binding of the PNA ligand to complementary DNA/RNA sequences, which is key to the importance of PNAs, conferring stronger hybridisation affinity to DNA/RNA compared to native DNA. This property facilitates the application of PNAs in techniques such as single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) detection, fluorescent in-situ hybridisation (FISH) and molecular biosensors, in the molecular diagnostic and research sectors.
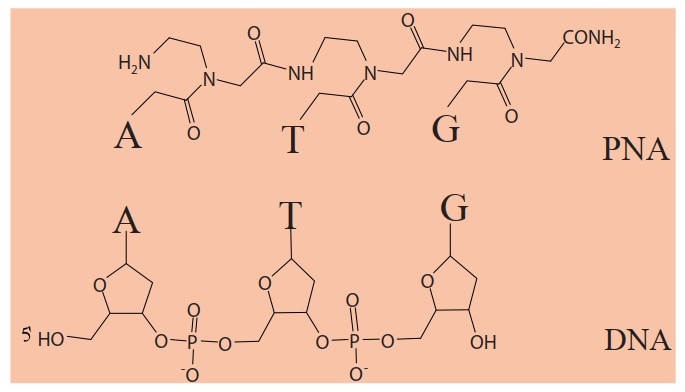
Fig. 1 Comparison of PNA and DNA illustrating differences in the backbone structure
Benchtop MALDI-TOF MS "MALDI-8020"

Key features:
- Linear mode (positive ion) MALDI-TOF
- 200 Hz solid-state laser, 355 nm
- Load-lock chamber for fast sample introduction
- UV laser-based source cleaning (patented)
- Small footprint/benchtop design
- Quiet operation (<55 dB)


