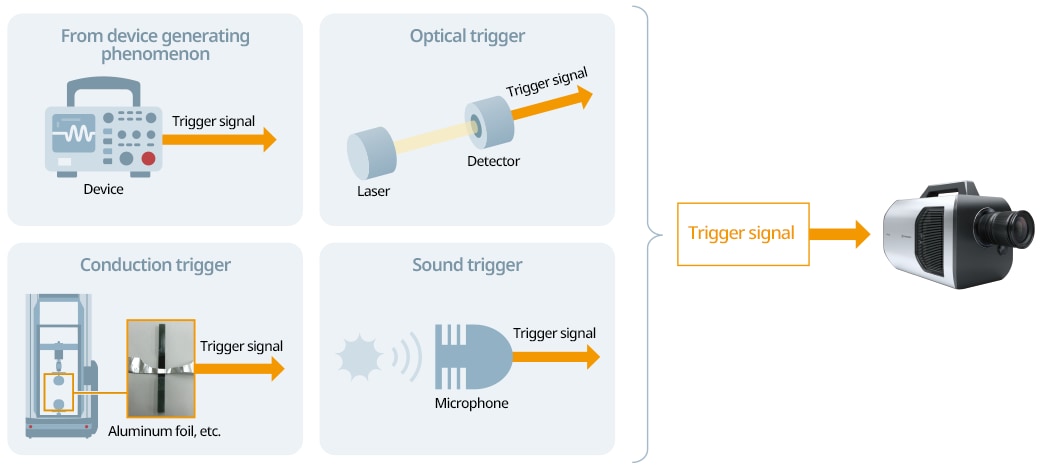
Types of High-Speed Video Cameras
Readout Method (Typical High-Speed Video Cameras)
In a typical high-speed camera, the memory for storing video images is located separate from the image sensor, and image signals are sequentially transferred from each sensor pixel to the memory. However, because the signal transfer rate is limited, the image resolution decreases as the recording speed increases.
Sequential Transfer of Video Signals from Each Pixel to the Memory
-
Low Recording Speed
Because the time interval between images or frames is long, a large number of pixels can be transferred per frame
-
High Recording Speed
Pixel volume that can be transferred per frame is limited due to a restricted signal transfer rate.
Burst Method (HPV Series)
The burst method provides sufficient memory for the frame rate capacity directly on the image sensor and links every pixel to this memory through individual connections. Video signals stored in the memory during recording are then transferred externally once recording has ended.
Comparison of the Burst Method and Readout Method
The boundaries of the respective effective areas of the burst and readout methods range from approximately several hundred kfps to 1 Mfps.