Shimadzu Contribution Thus Far and SDGs
Even before the SDGs were adopted, Shimadzu has been facing societal challenges head-on and has been directly and indirectly involved in solving those challenges through our business activities, based on our corporate philosophy "Contributing to Society through Science and Technology."
However, given that the SDGs specify goals and targets in specific terms, we have been making the relationship between our measures thus far and solving societal challenges more apparent.
Doing so has revealed just how many of our businesses are related to societal challenges and involved in solving them, which reconfirms that the direction of our businesses thus far has been consistent with society. Additionally, we worked on "visualization" for resolving social issues through specific business activities, for the future of 2030 envisioned by the SDGs. In addition to our existing businesses, we have reviewed our future strategic CSR activities (Solving social issues through business) and fundamental CSR activities (Responsible activities as a member of society). This will accelerate our efforts to create shared value.
Background of Activities Involving SDGs

How Company Activities Relate to SDGs

Distribution of Contribution to SDGs (Change from Past to Future)
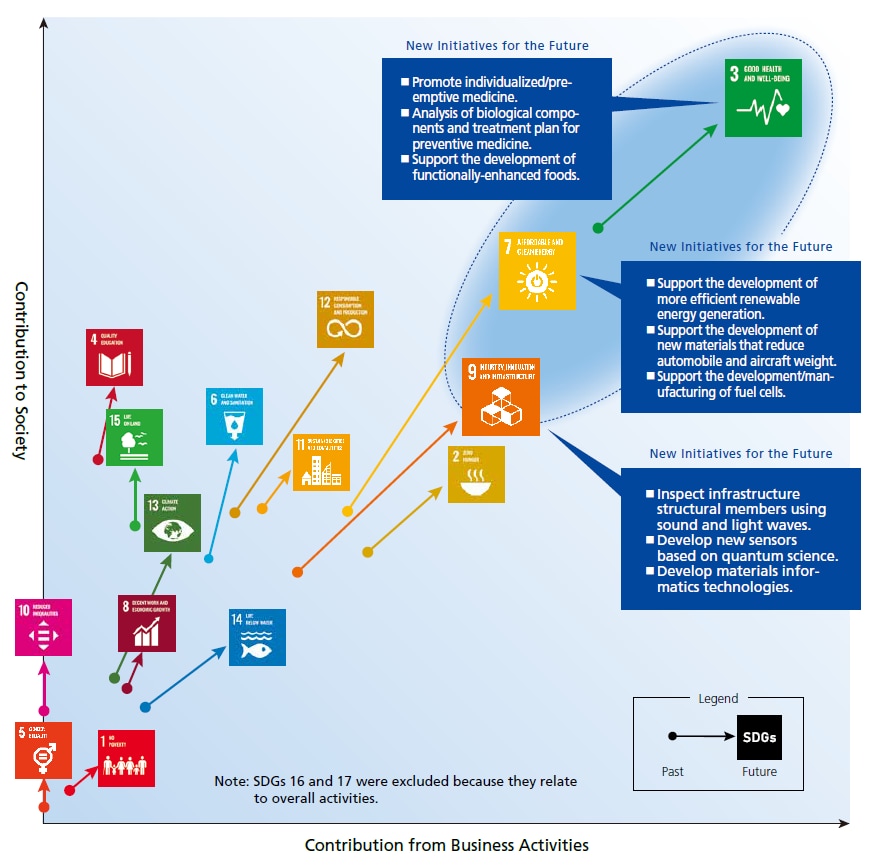
This distribution chart was created to organize employees' perceptions of SHIMADZU. Regarding "Engaging in activities as a responsible member of society (CSR)", there was a discrepancy between external evaluations and employee perceptions. We believe this is because even high external evaluations are sometimes taken for granted within the company.
Here's how to create it:
(1) For each of the 169 targets, from the perspective of "Engaging in activities as a responsible member of society (CSR)" and "Solving the challenges of society through business operations (CSV)", all divisions listed two themes; themes we are currently working on and themes we are going to tackle in the future.
(2) The themes listed were divided into 3 levels of importance: high, medium, and low. The scores were added for each of the 17 goals from the two perspectives of CSR and CSV.
(3) The horizontal axis represents the score of CSV, and the vertical axis represents the total score of CSR and CSV. For each of the 17 targets, the score of the themes currently being addressed is indicated by a circle on the distribution chart.
(4) The horizontal axis is the score of CSV, and the vertical axis is the total score of CSR and CSV. For each of the 17 targets, the sum of the scores of the themes currently being addressed and those that will be addressed in the future is indicated by the SDGs logo on the distribution chart.
(5) For each of the 17 targets, the change from (3) to (4) is indicated by arrows.
Results from SDG Target-Level Measures
|
Target |
Targets |
Shimadzu Measures Thus Far(Examples) |
|---|---|---|
 |
3.2 |
|
| 3.3 By 2030 end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, and neglected tropical diseases and combat hepatitis, water-borne diseases, and other communicable diseases. |
||
|
3.4 |
|
|
|
3.5 |
|
|
|
3.6 |
|
|
|
3.9 |
|
|
 |
6.3 |
|
 |
7.3 |
|
 |
11.4 |
|
|
11.6 |
|
|
 |
12.4 |
|
 |
8.7 |
|
|---|
Creating Shared Value by Treating SDGs as Business Opportunities
from an Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Perspective
In addition to considering how SDGs relate to our businesses, we also considered how SDGs affect the way we manage our businesses throughout the entire value chain, so that we treat SDGs as important business opportunities for future business operations. We believe doing so will clarify which challenges should be prioritized in the future.
Since SDGs involving challenges of a global scale can also be considered challenges for Shimadzu's business areas of "human health," "safety and security of society," and "industrial development," we believe that providing innovative and useful solutions for such challenges will also result in expanded business.
On the other hand, they can have more than a slight negative effect on the value chain. However, even in the case of such challenges, we think such negatives can be changed to positives by considering ways to create a sustainable society, such as by improving quality, improving operability, or increasing brand strength.


SHIMADZU’s SDGs badge made from "Shimadzu Forest" thinned wood

We created our own SDGs badge made from wood thinning from the "Shimadzu Forest" (Yagi-cho, Nantan City, Kyoto Prefecture), where we have been participating in Forest cultivation activities since 2008. The aim of this production is to raise awareness of the SDGs both internally and externally. Employees who have understood the relationship between the SDGs and SHIMADZU through in-house e-learning and workshops wear this SDGs badge. Through this initiative, this SDGs badge have been provided to more than 1500 employees and distributors throughout the Shimadzu Group.
The badges are manufactured at a woodworking shop in Kyoto. It means that SHIMADZU contributes to the conservation of local ecosystems and the promotion of forestry industry (Contribution to “SDGs Goal 15: Life on Land”). In addition, we also contribute to “SDGs Goal 8: Decent work and economic growth" by having people with disabilities participate in the badge production process.


